Looks and Life: A summary of the study
23 August 2019
Looks and Life: A summary of the study
What we wanted to learn
We were interested in how people with a health condition that affects their appearance deal with difficult thoughts and feelings about their appearance. We know from previous research that some people avoid activities that they expect will bring up difficult thoughts and feelings, and some spend a lot of time and energy covering, concealing and focusing on their appearance. We wanted to learn more about two mental tendencies: (1) a desire to get rid of or avoid difficult thoughts and feelings (called ‘experiential avoidance), and (2) getting caught up with difficult thoughts (called ‘cognitive fusion’). Specifically, we wanted to know whether these two tendencies might explain why people with conditions that affect their appearance are more or less likely to (a) avoid stressful appearance-related activities, and (b) to cover, conceal and focus on their appearance.
What we did
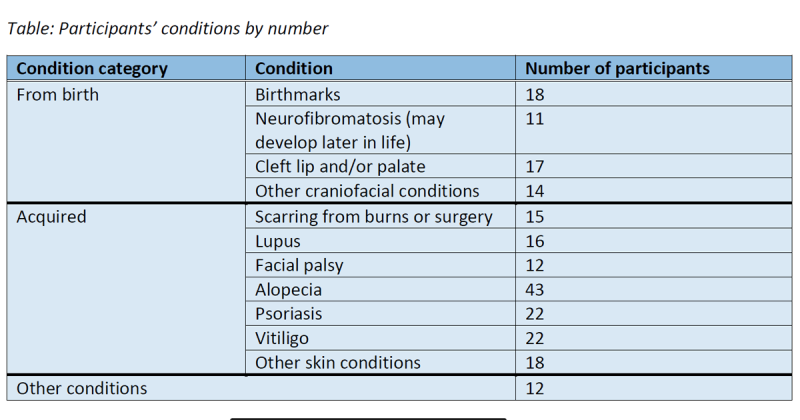
To do this, we asked charities and organisations from the Appearance Collective to help us recruit participants across a wide range of appearance-affecting conditions (a breakdown by condition type is given below). Thanks to these organisations, we surveyed 220 adults, aged 18-75, just under 80% of whom were female. Participants completed demographic questions, a series of validated psychological questionnaires, and gave details about how their condition affects their appearance. We ran statistical analyses called Mediation analyses, to find out how well (1) experiential avoidance and (2) cognitive fusion statistically explained participants’ tendency to (a) avoid stressful appearance-related situations and (b) cover, conceal and focus on their appearance. In the analyses, we took account of participants’ age, gender, how visible they perceived their different appearance to be to others, and whether their condition was acquired or from birth.
What we found
We found that participants’ level of (1) experiential avoidance (a tendency to try and get rid of or avoid difficult thoughts and feelings) did partly explain their tendency to (a) avoid stressful appearance-related situations. The more experientially avoidant they were, the more likely they were to avoid stressful situations. Experiential avoidance didn’t, though, explain participants’ tendency to (b) cover, conceal and focus on appearance. On the other hand, participants’ level of (2) cognitive fusion (getting caught up in thoughts) explained both (a) avoiding stressful situations and (b) cover, concealing and focusing on appearance. The more participants were caught up in thoughts, the more they’d avoid stressful situations, and the more they’d cover, conceal and focus on their appearance.
What this means
We now know that these two mental tendencies are likely to play a role in how people cope with difficult thoughts and feelings about their appearance. Many types of psychological therapy (like traditional cognitive behavioural therapy) try to help people manage distress by teaching them to change their thinking patterns from less rational to more rational. What the findings of the study suggest is that they may be another way: Learning to just observe thoughts as thoughts rather than facts (‘cognitive defusion’) and learning to open up to and tolerate difficult thoughts and feelings (‘experiential acceptance’), without trying to change those internal experiences, may help people with appearance-affecting conditions engage more in meaningful activities that they may otherwise avoid. An approach called Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (or ‘ACT’) focuses on developing cognitive defusion and experiential acceptance, and we at CAR are currently developing a self-help programme based on ACT that we would like to test in the near future.
Filter News

Manchester Comedy Night
Manchester's Frog & Bucket Comedy Club hosted the 2nd date on the NTUK 2022 comedy circuit
Read More
Call for evidence for new 10-year plan to improve mental health
The government has committed to develop a new cross-government, 10-year plan for mental health and wellbeing
Read More
Medical Photography of dermatological conditions - research
Research study: Patient perceptions of medical photography of dermatological conditions
Read More
#BackThe1in6
Read the My Neuro Survey findings from the Neurological Alliance & sign the petition for a Neuro Taskforce to deliver change
Read More
Austin’s NF1 story
Austin's mother, Katie, describes how local biker clubs have helped to support Austin since his NF1 diagnosis
Read More
NTUK Comedy Circuit 2022
Three more dates for your diary: Manchester 14/6, Newcastle 12/7, Glasgow 14/7. Altogether now: "Happy birthday NTUK!"
Read More
RideLondon-Essex 2022
Thank you to our RideLondon-Essex 2022 cyclists! Click here for some great photos from the day
Read More
Pat’s Triathlon Challenge
Pat is taking on a 3 day triathlon style challenge to raise awareness & funds for Neurofibromatosis research & support
Read More
World Neurofibromatosis Type 2 Day and 40 Years of NTUK
A celebration and call out to get involved, ask questions and join the community with Emily Owen
Read More
